Ball screw drive
Ball screw drive link properties implement a ball screw drive. Only the linear elastic behaviour is modelled, non-linearities are neglected. The simplifications are:
- any kind of backlash is neglected
- local deformation of the nut is not modelled
Definition
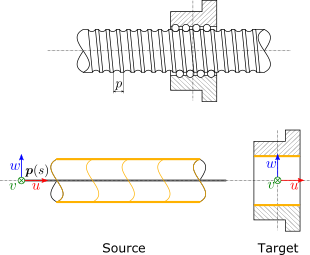
Source and target interfaces should be chosen as shown in following figure:
Source interface
| Type |
Moving interface (Fourier) |
| Topologies |
Peripheral face of the screw |
| Location |
Along the screw axis |
| u direction |
Axial, along the screw axis |
| v direction |
Radial |
| w direction |
Radial |
Target interface
| Type |
Stationary interface (6dof) |
| Topologies |
Mounting face of the nut |
| Location |
Center of the screw axis |
| u direction |
Axial, along the screw axis |
| v direction |
Radial |
| w direction |
Radial |
Recommended link settings
| Use ground for source |
unchecked |
| Location master |
target |
| Orientation master |
either source or target |
Parameters
| Parameter |
Unit |
Description |
|---|
| Screw pitch |
m |
Pitch of the ball screw |
| Axial stiffness |
N/m |
Axial stiffness of the nut-to-screw coupling |
| Radial stiffness |
N/m |
Radial stiffness of the nut-to-screw coupling |
| Tilting stiffness |
Nm/rad |
Tilting stiffness of the nut-to-screw coupling |
| Axial damping |
Ns/m |
Axial damping of the nut-to-screw coupling |
| Radial damping |
Ns/m |
Radial damping of the nut-to-screw coupling |
| Tilting damping |
Nms/rad |
Tilting damping of the nut-to-screw coupling |
| Rotational damping |
Nms/rad |
Rotational damping when rotating the screw relative to the nut |