Gear drive¶
Gear drive link properties implement a toothed gear drive. Only the linear elastic behaviour is modelled, non-linearities are neglected. The simplifications are:
any kind of backlash is neglected
the force pushing the gears apart (due to the pressure angle of the teeth) is not modelled and has to be added as load in an analysis if desired
irregular transmission due to the teeth is not modelled
local deformation of the gears is not modelled
Definition¶
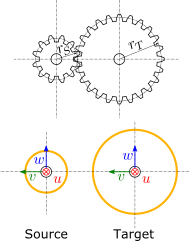
Source and target interfaces should be chosen as shown in following figure:
Source interface¶
Type |
Stationary interface (6dof) |
Topologies |
Peripheral face of the source gear |
Location |
Center of the source gear |
u direction |
Axial, along the axis of rotation of the source gear |
v direction |
Aligned with the v-direction of the target gear |
w direction |
Resulting direction |
Target interface¶
Type |
Stationary interface (6dof) |
Topologies |
Peripheral face of the target gear |
Location |
Center of the target gear |
u direction |
Axial, along the axis of rotation of the target gear |
v direction |
Aligned with the v-direction of the source gear, either pointing from the target to the source gear or vice versa |
w direction |
Parallel to the w-direction of the source gear |
Recommended link settings¶
Use ground for source |
unchecked |
Location master |
none |
Orientation master |
either source or target |
Parameters¶
Parameter |
Unit |
Symbol |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Source gear radius |
m |
\(r_S\) |
Radius of the pitch line of the source gear |
Target gear radius |
m |
\(r_T\) |
Radius of the pitch line of the target gear |
Contact stiffness |
N/m |
\(k\) |
Stiffness of the contact between the gears including tooth compliance |
Contact viscous damping |
Ns/m |
\(d_v\) |
Viscous damping of the contact between the gears including tooth compliance |
Contact hysteretic damping |
None |
\(d_h\) |
Hysteretic damping of the contact between the gears including tooth compliance |